With a substantial decrease observed in streamflow gages across the world (Stokstad, 1999), remote sensing can provide valuable observations for estimating runoff in ungauged basins. A simple approach is to estimate the runoff in basins using the water balance approach. The water balance of a basin is given by
[Change in Storage (ds/dt)] = Precipitation (P) - Evapotranspiration (ET) - Runoff (Q)]
In the water balance equation, ds/dt, P and ET are quantities that can be remotely sensed, allowing the inference of runoff and also the study of the hydrologic characteristics of data-scarce catchments.
Objectives
The main objectives of this exercise are:
- To estimate and validate the runoff of basins using publicly available remotely sensed P, ET, and ds/dt datasets
- To study the hydrologic characteristics of basins using runoff ratio (RR), aridity index (AI), and evaporative index (EI).
The study areas examined are the following river basins:
- Amazon
- Mississippi
- Nile
The time period of January 2004 to December 2006 (with monthly time step).
Proposed Methods and Data
- Preprocessing of Data: Download and preprocess P, ET, and ds/dt datasets. Datasets: TRMM 3B42RT (P), GLEAM (ET), GRACE (ds/dt), Pan et al. (2012) (ground truth data for all variables). Basin-averaged time series should be calculated not spatial maps.
- Estimation and Validation of Runoff: Use the water balance equation (see above) to estimate runoff and compare the estimate to the observed streamflow.
- Estimation of Basin Characteristics: Compare the three basins using RR, AI, and EI.
Testing
Remote sensing provides observations for estimating runoff in ungauged basins using a simple water balance approach. The water balance of a basin is given by ds/dt = P - ET - Q. Change in storage, precipitation and evapotranspiration are quantities that can be remotely sensed, allowing for the inference of runoff.
The study areas in this example include the Amazon, Mississippi, and Nile river basins. The time period under consideration is January 2004 to December 2006 (with Monthly time steps). Precipitation, evapotranspiration, and change in storage datasets were downloaded and preprocessed then basin-averaged time series were calculated. The datasets studied include TRMM 3B42RT (precipitation), GLEAM (evapotranspiration), GRACE (change in storage over time), and Pan et al. (2012) for ground truth data for all variables.
The water balance equation was used to estimate runoff and compare the estimate to the observed streamflow. The estimates and validations were made using publicly available remotely sensed precipitation, evapotranspiration, and change in storage datasets.
The hydrologic characteristics of the three basins were studied and compared using the runoff ratio (RR), aridity index (AI), and evaporative index (EI). This can be achieved using the following equations for basin characteristics:
- Runoff Ratio (RR) = Runoff (Q) / Precipitation (P)
- Aridity Index (AI) = Potential Evapotranspiration (Ep) / Precipitation (P)
- 0.0 < AI < 1.0 - Humid basin
- 1.0 < AI < 2.0 - Temperate basin
- AI > 2.0 - Arid basin
- Evaporative Index (EI) = Actual Evapotranspiration (E) / Precipitation (P)
Sample R Code
rm(list=ls())
# set working directory
setwd("/Users/<user>/.../Data/")
# load required libraries
library("raster")
# load the GRACE data
grace = brick("GRCTellus.JPL.200204_201701.LND.RL05_1.DSTvSCS1411.nc")
# rotate the GRACE data
grace = rotate(grace)
# AMAZON river basin
# load the required shapefile
shp_amazon = shapefile("amazon.shp")
# add projection to shapefile
projection(shp_amazon) = projection(grace)
# extract the mean values
grace_amazon = extract(grace, shp_amazon, mean, na.rm=TRUE)
grace_amazon = c(grace_amazon)
grace_amazon = grace_amazon[19:54]
# ds/dt
grace_dsdt = diff(grace_amazon)
View(grace_amazon)
View(grace_dsdt)
# NILE river basin
# load the required shapefile
shp_nile = shapefile("nile_el_ek.shp")
# add projection to shapefile
projection(shp_nile) = projection(grace)
# extract the mean values
grace_nile = extract(grace, shp_nile, mean, na.rm=TRUE)
grace_nile = c(grace_nile)
grace_nile = grace_nile[19:54]
# ds/dt
grace_dsdt = diff(grace_nile)
View(grace_nile)
View(grace_dsdt)
# MISSISSIPPI river basin
# load the required shapefile
shp_mississippi = shapefile("mississippi.shp")
# add projection to shapefile
projection(shp_mississippi) = projection(grace)
# extract the mean values
grace_mississippi = extract(grace, shp_mississippi, mean, na.rm=TRUE)
grace_mississippi = c(grace_mississippi)
grace_mississippi = grace_mississippi[19:54]
# ds/dt
grace_dsdt = diff(grace_mississippi)
View(grace_mississippi)
View(grace_dsdt)Results
A summary of the compiled results from the above scripts can be found below:
| amazon | ds/dt | nile | ds/dt | mississippi | ds/dt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg | -1.829 | 0.000 | -0.789 | -0.002 | -0.523 |
| Max | 17.782 | 12.191 | 5.975 | 4.303 | 6.559 |
| Min | -19.889 | -9.186 | -6.135 | -5.479 | -8.904 |
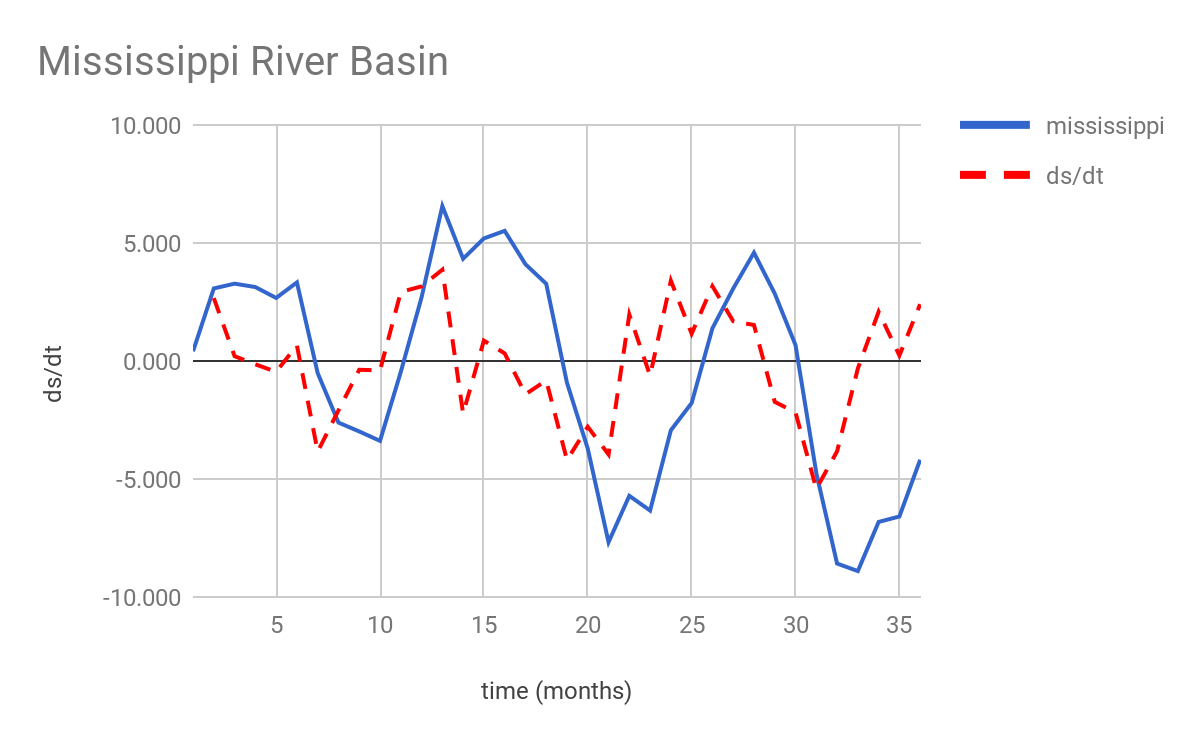
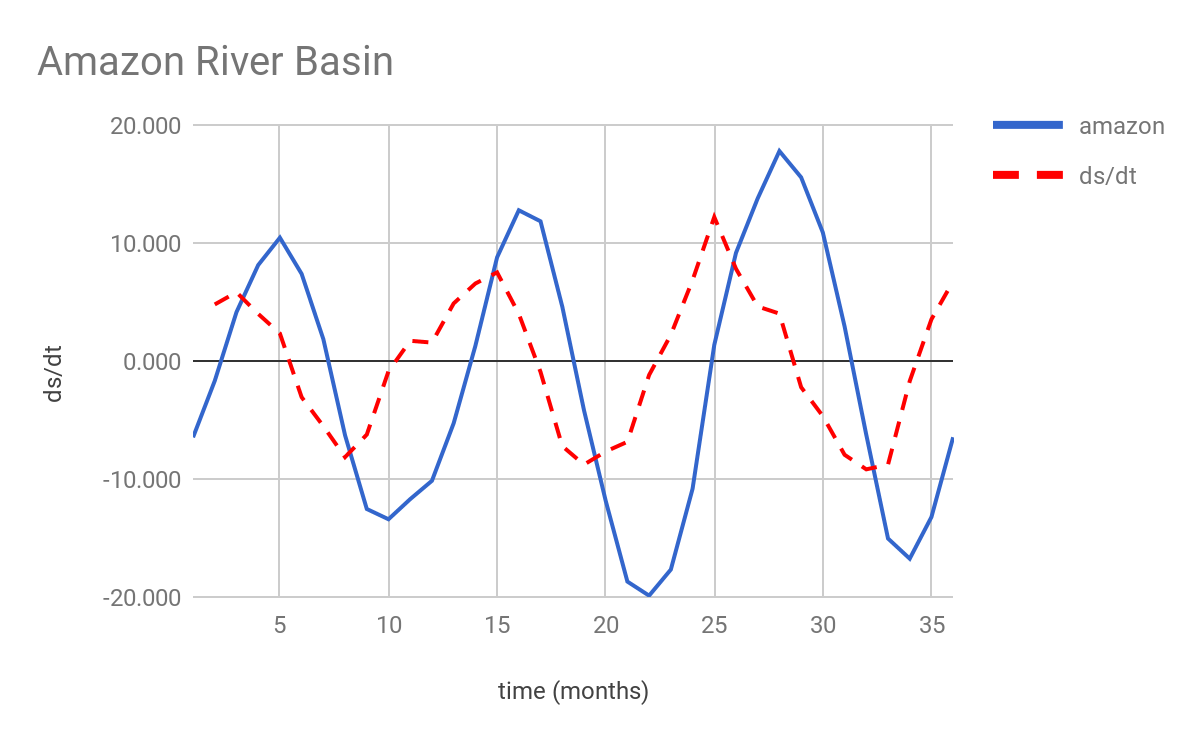
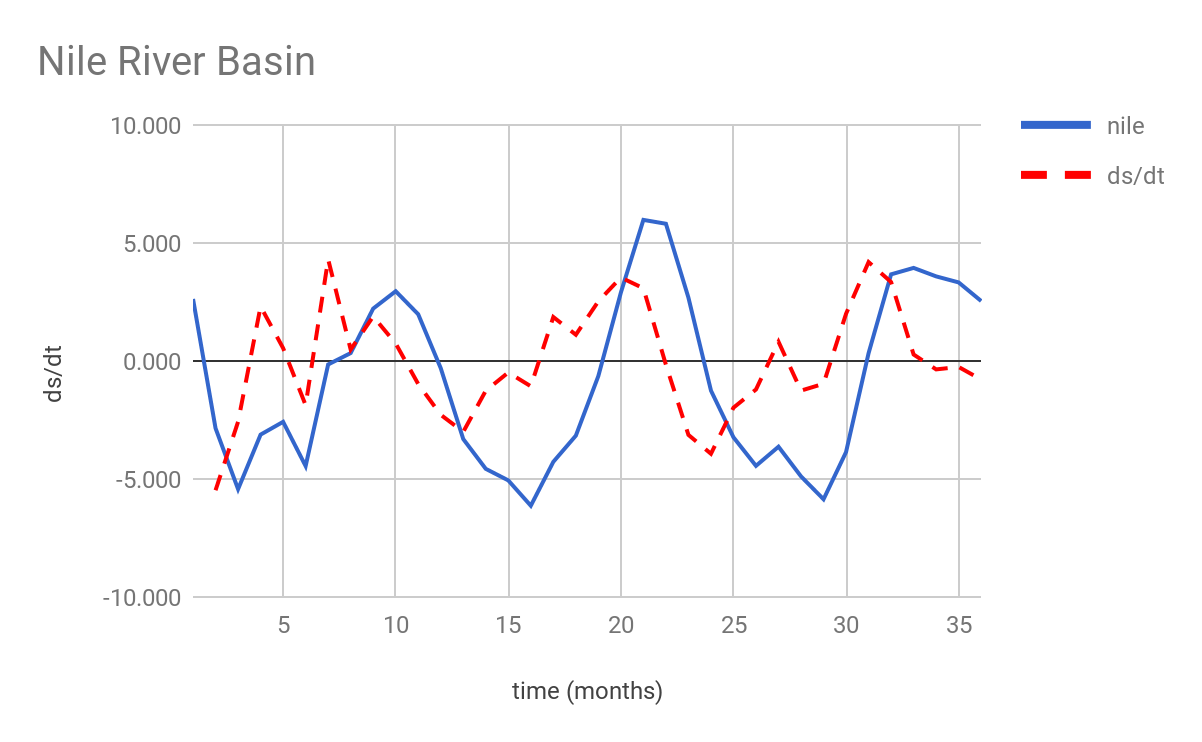
References
Pan, M., A.K. Sahoo, T.J. Troy, R.K. Vinukollu, J. Sheffield, and E.F. Wood, 2012: Multisource Estimation of Long-Term Terrestrial Water Budget for Major Global River Basins. J. Climate, 25, 3191–3206, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00300.1
Stokstad, E. (1999). Scarcity of rain, stream gages threatens forecasts. Science, 285(5431), 1199– 1200. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5431.1199
GRACE data, https://grace.jpl.nasa.gov/data/get-data/monthly-mass-grids-land/